In recent years, the use of Ground Penetrating Radar technology, or GPR techniques, has emerged as a transformative tool in the field of environmental evaluation and infrastructure development. This nonintrusive technology enables specialists to visualize and analyze what lies beneath the surface without the need for large-scale excavation. As concerns about eco-friendliness and protection grow, understanding the importance and benefits of Ground Penetrating Radar surveys becomes crucial for experts across various fields.
From detecting underground utilities to evaluating geotechnical conditions, GPR technology have proven invaluable in making knowledgeable choices. They not only improve project effectiveness but also help lessen risks associated with unexpected subsurface conditions. As we delve deeper into the intricacies of GPR technology, its applications, and its role in today’s industry, we aim to provide a comprehensive overview for those seeking to make use of this effective tool in their projects.
##### Grasping GPR Surveys
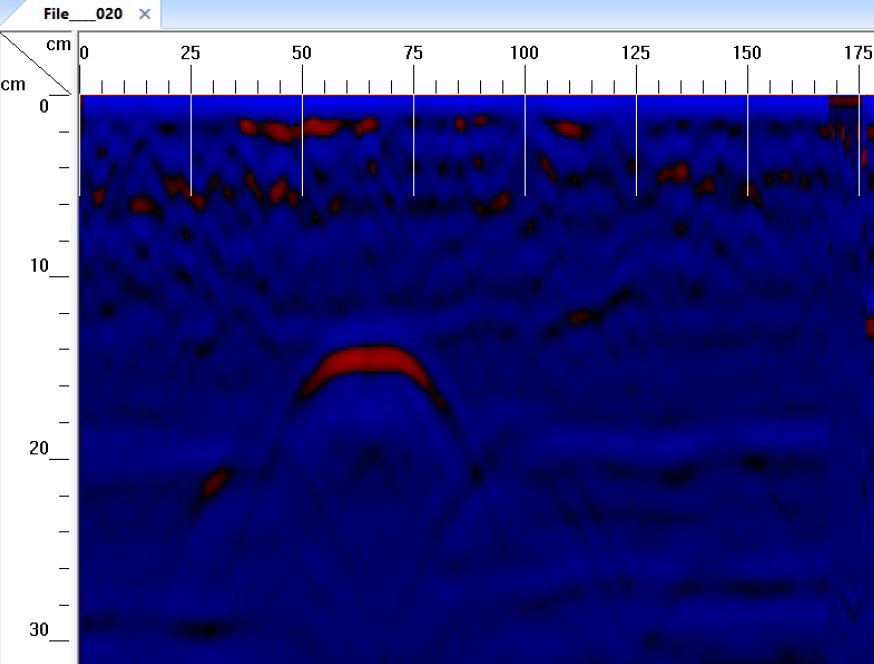
GPR is a non-destructive geophysical technique which uses radar signals to visualize the subsurface . The method leverages high-energy EM waves transmitted into the ground , which reflect off various subterranean substances. Through examining the reflected data, professionals can produce comprehensive images of the subsurface formations, including utilities , voids , and other anomalies . This technology is renowned for its capability to provide immediate information and visualizations , making it an essential tool in multiple fields such as engineering , ecological evaluation, and historical research.
One of the core advantages of Ground Penetrating Radar investigations is their flexibility. They can probe numerous types of soil and materials , from concrete and asphalt to stone and gravel. This flexibility allows for thorough assessments in varied environments. Additionally, this hyperlink can function with minimal disruption to the surface , making them appropriate for urban environments , building projects, and sensitive environmental areas . As a result , stakeholders can obtain vital subsurface data without significant disturbance to existing systems or ecosystems .
The value of Ground Penetrating Radar surveys spans across various industries , as they furnish essential information for informed choices and planning management . In building and design, for instance , GPR can detect underground lines and construction flaws, avoiding costly damage and delays during undertakings. In environmental assessments , it assists in identifying pollution or changes in earth formations . Overall , this technology enhances the understanding of what lies beneath the surface , enabling educated decisions that promote security and efficiency .
Benefits and Applications of GPR
GPR offers various benefits, particularly in the field of subsurface analysis. One of the key advantages is its non-invasive characteristics, allowing for in-depth imaging of the underground without disrupting the ground. This feature is crucially important in urban settings, where minimizing disruption is vital. Additionally, GPR can provide live data, enabling more rapid decision-making and more efficient project planning. Its ability to detect a range of materials, including metals, plastics, and soils, enhances its flexibility in multiple investigative scenarios.
GPR is extensively utilized in multiple industries, with significant applications in construction and civil engineering. By identifying the presence of subsurface utilities, potential obstacles, and defects, GPR assists in minimizing risks associated with excavation and construction. This technology also plays a essential role in environmental studies, providing insights into the makeup of soils and pollutants, which is essential for remediation efforts and land evaluation. Furthermore, its applications reach to archaeology, where GPR helps discover ancient artifacts and interpret historical structures without excavation.
The adoption of GPR technology in infrastructure inspections is transforming maintenance practices. By detecting structural issues such as cracks, voids, and corrosion beneath surfaces, GPR helps with proactive maintenance and safety protocols. This capability not only enhances the durability of infrastructure but also boosts public safety and cost management. As improvements in GPR continue, its scope of usage is expected to increase, establishing it as a critical tool for multiple fields that rely on precise underground data.
Selecting and Conducting GPR Investigations
Selecting the appropriate GPR survey provider is crucial for ensuring accurate and reliable results. When selecting a company, evaluate their experience, equipment quality, and specialization in the particular field needed for your project. Analyzing past works and client testimonials can offer perspective into their capabilities. Engaging GPR Survey Bromsgrove that is familiar with the local legal environment and has knowledge with similar survey conditions can further enhance the project's effectiveness.
Once you have selected a GPR provider, the following phase involves organizing the survey itself. This includes defining the survey area, evaluating the site environment, and understanding the goals of the investigation. Collaboration with the investigation team is essential to establish the most effective survey approach, such as layout and scan depth, to meet project objectives. Tackling any logistical issues upfront, such as access issues and site safety, will contribute to a more seamless survey process.
The actual conduct of a GPR survey typically follows a structured methodology. It begins with a site visit to install and adjust the tools, followed by data collection where the GPR device is moved across the designated area. The data is then processed and interpreted to uncover subsurface details. Frequent communication between the investigation team and stakeholders ensures that any observations during the survey are documented and can influence ongoing or future work, reinforcing the overall importance of GPR investigations in uncovering critical information about the subsurface condition.
